Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Running pyAFQ using the GPU for tractography#
Running pyAFQ using the GPU for tractography is as simple as
(1) Installing GPUStreamlines using pip install and
(2) passing in the tractography_ngpus parameter when you create your
GroupAFQ object.
- To install GPUStreamlines, do:
pip install git+https://github.com/dipy/GPUStreamlines.git
That’s step 1 complete! The rest of this example is the same as the GroupAFQ
example except with the tractography_ngpus parameter set.
from AFQ.api.group import GroupAFQ
import AFQ.data.fetch as afd
import os.path as op
import plotly
We start with some example data. The data we will use here is generated from the Stanford HARDI dataset. We then setup our myafq object which we will use to demonstrate the clobber method.
afd.organize_stanford_data()
tracking_params = dict(n_seeds=1000000,
random_seeds=True,
rng_seed=2025,
trx=True)
Running with the GPU#
We will use the GPU for tractography. This is done by passing in tractography_ngpus That’s it!
myafq = GroupAFQ(
bids_path=op.join(afd.afq_home, 'stanford_hardi'),
preproc_pipeline='vistasoft',
tracking_params=tracking_params,
tractography_ngpus=1)
# From here, pyAFQ should run normally
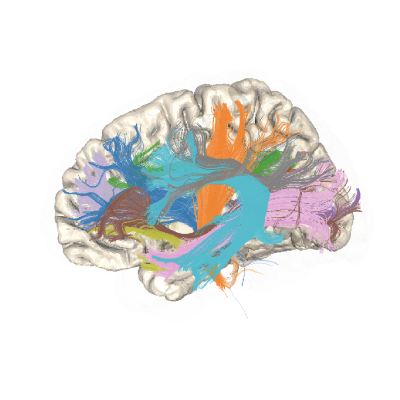
bundle_html = myafq.export("all_bundles_figure")
plotly.io.show(bundle_html["01"][0])
Estimated memory usage: 0 MB